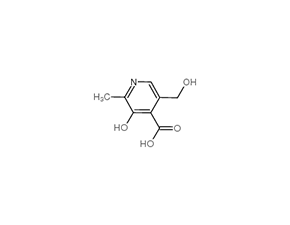
4-Pyridoxic Acid
CAS No. 82-82-6
4-Pyridoxic Acid( —— )
Catalog No. M19152 CAS No. 82-82-6
4-Pyridoxic Acid, a catabolite of vitamin B6, is a water-soluble B-group vitamin that can be used as a urinary diagnostic biomarker for determining the nutritional status of these vitamins.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 26 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-Pyridoxic Acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-Pyridoxic Acid, a catabolite of vitamin B6, is a water-soluble B-group vitamin that can be used as a urinary diagnostic biomarker for determining the nutritional status of these vitamins.
-
Description4-Pyridoxic Acid, a catabolite of vitamin B6, is a water-soluble B-group vitamin that can be used as a urinary diagnostic biomarker for determining the nutritional status of these vitamins.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorVB6
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number82-82-6
-
Formula Weight183.16
-
Molecular FormulaC8H9NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 5 mg/mL (27.30 mMult)
-
SMILESCC1=NC=C(C(=C1O)C(=O)O)CO
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Shibata K, et al. Urinary excretion levels of water-soluble vitamins in pregnant and lactating women in Japan[J]. Journal of Nutritional Science & Vitaminology, 2013, 59(3):178-86.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Itaconate-alkyne
Itaconate-alkyne is a bioorthogonal probe for quantitative and site-specific chemoproteomic profiling of itaconate in inflammatory macrophages and enables biochemical evaluation and proteomic analysis of its direct targets.
-
Citral
Citral is a clear yellow colored liquid with a lemon-like odor. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.
-
MI-3454
MI-3454 is an orally active, selective and potent inhibitor of Menin-MLL1 interaction that inhibits the proliferation and induces differentiation of acute leukemia cells with MLL1 translocation or NPM1 mutation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


